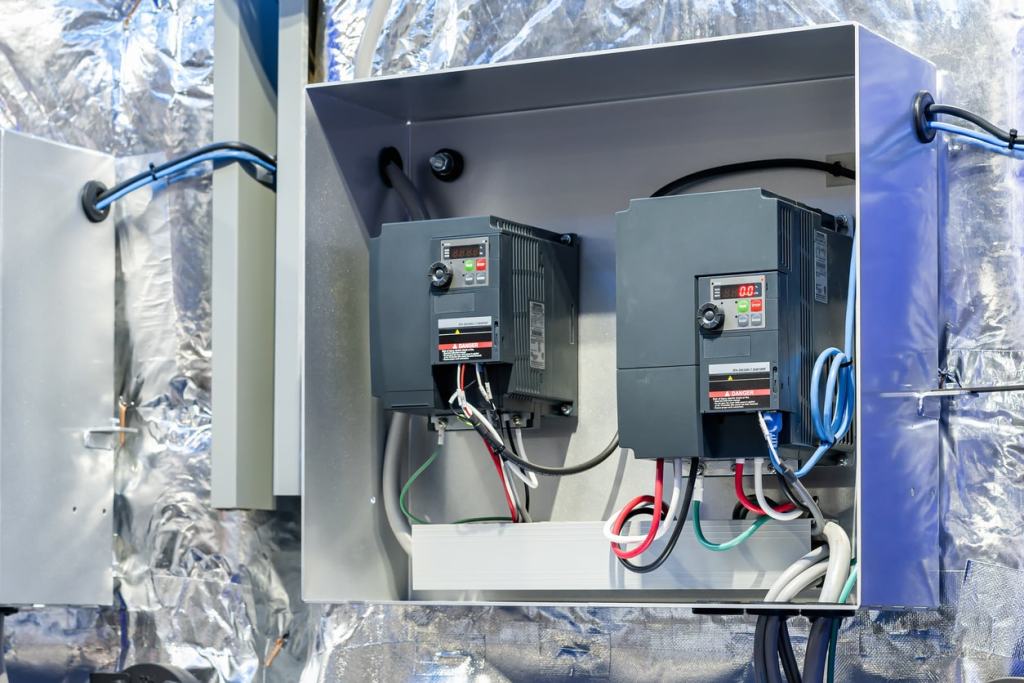
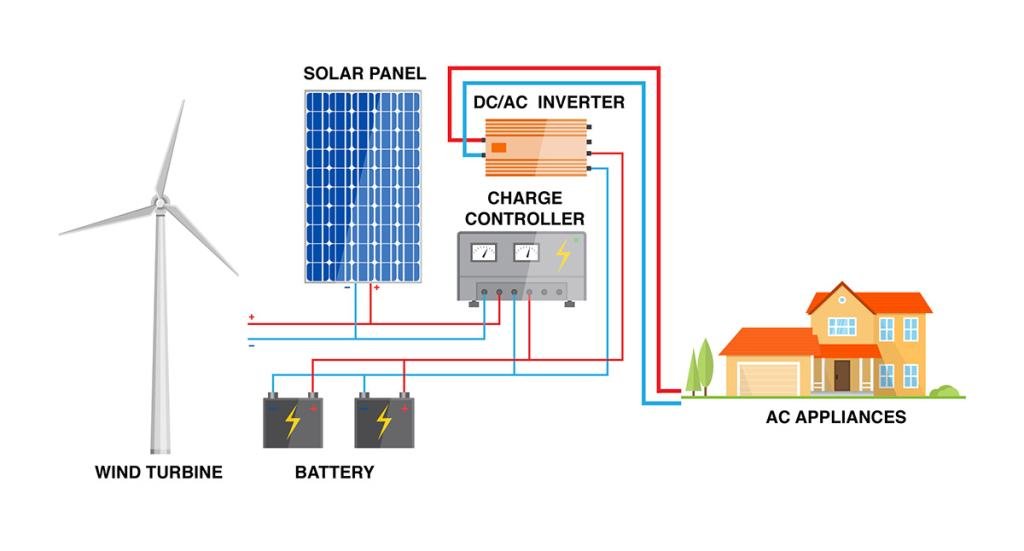
inverter is an electrical device that converts and controls electrical energy. In technical terms, here’s how an inverter functions:
- DC to AC Conversion: An inverter typically takes direct current (DC) from a source, such as a battery or a photovoltaic solar panel, and converts it into alternating current (AC). This conversion process often involves high-frequency switching techniques.
- Waveform Generation: Inverters are capable of generating different types of AC waveforms. The most common is a sinusoidal waveform, but inverters can also produce square waves or modified sine waves, depending on the application.
- Voltage and Frequency Control: Inverters can control the output voltage and frequency to match the requirements of the connected loads. This adjustability allows them to be used in a wide range of applications.
Inverters find applications in various fields:
- Solar Power Systems: Inverters are used to convert the DC electricity generated by photovoltaic solar panels into usable AC electricity for homes or businesses.
- Electric Vehicles: In electric vehicles, inverters convert DC power from the battery into AC power required for the vehicle’s motor operation.
- Industrial Applications: In factories, inverters are used to control machines or motors, allowing for precise adjustment of motor speed and torque.
- Wind Power Systems: Inverters are used to convert the variable-speed DC electricity generated by wind turbines into stable AC electricity for the grid.
- Backup Power Sources: Inverters can serve as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to provide AC power during electrical outages.
Inverters play a crucial role in energy conversion and control in various applications. Their technical design, operation, and control can be complex and are typically developed and operated by electrical and electronics engineers.