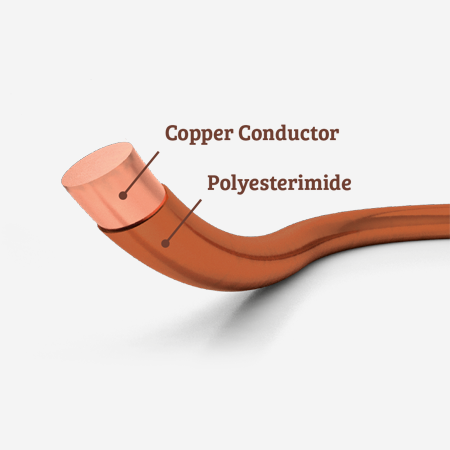
Providing thermal resistance up to 180°C, EmTherm 180, offers strength against freon gas and good resistance against solvents. It also possess the features of high speed rolling capability and high mechanical resistance.
Fields of Use:
- Oil transformers
- Transformers withcasting resin
- General purpose electric motors
- Voltage regulators.
| Thermal Class (°C) | Class HB, 180 °C |
| Insulation | Base Coat | THEIC Modified Polyesterimide |
| Insulation | Top Coat | - |
| Insulation | Bond Coat | Aromatik Poliamid |
| Production Range (mm) (mm) | 0.08 – 1.30 mm |
| Certification I.E.C | IEC 60317 - 37 |
| UL File No | |
| Class Temerature (°C) | 180 °C |
| Heat Shock (°C) | ≥ 200 °C |
| Cut Through Temperature (°C) | ≥ 320 °C |
| Solderability (°C) | Non solderability |
| Bonding Temperature (°C) | 160 °C - 190 °C |
| Re-Softening Temerature (°C) | > 190 °C |
| Normal Solvent Resistance | 4H |
| Dipping Varnish Resistance | Good |
| Refrigerant Resistance | Good |
| Transformer Oil Resistance | Non Usable |
| Distinct Features | Handling Equipment, Transformers, Motors |
| Fields of Use | Bondable by eff max. 120 A/mm2 or alchol/ soproply, Bondable by oven (160°C - 190°C), High mechanical resistance, Self Solderable Wire |
Copper Enamel Wire, Technical Insights and Applications
Enamel-coated coil wire, also known as magnet wire or winding wire, is a type of electrical wire made from a conductive core, typically copper or aluminum, which is coated with a thin layer of enamel insulation. This enamel insulation serves to electrically isolate the wire and prevent electrical short circuits when the wire is coiled or wound into electromagnetic components, such as coils, inductors, transformers, or electromagnets.
Key technical points about enamel-coated coil wire include:
Wire Composition: The core of enamel-coated coil wire is typically made of high-conductivity copper or aluminum due to their excellent electrical properties.
Enamel Insulation: The enamel insulation, typically made of a thermosetting polymer or varnish, is applied to the wire through an extrusion or immersion process. This enamel coating provides electrical insulation and high-resistance properties.
Thermal Class: Enamel-coated coil wires are classified based on their thermal resistance capabilities. Different classes are designated by a number, indicating the maximum allowable temperature before the enamel insulation breaks down. Common thermal classes include 130°C, 155°C, and 180°C, among others.
Diameter and Gauge: Enamel-coated coil wire is available in various diameters and gauges to accommodate different applications. Thinner wires are used for fine winding, while thicker wires may be used for higher current-carrying applications.
Coils and Windings: Enamel-coated coil wire is widely used in the winding of coils, inductors, and transformers in electrical and electronic circuits. The enamel insulation allows for tight winding without risk of electrical contact between the turns.
High Insulation Resistance: The enamel insulation has high insulation resistance properties, making it suitable for applications where electrical isolation is crucial.
Durability: Enamel-coated coil wire is known for its durability and heat resistance, making it suitable for applications where elevated temperatures may be encountered.
Applications: It is used in a wide range of applications, such as electric motors, generators, solenoids, transformers, inductors, and speakers.
Enamel-coated coil wire is fundamental in the construction of electromagnetic components in electrical and electronic systems. Its ability to provide electrical insulation while maintaining high conductivity is essential for the efficient and reliable operation of these devices. The choice of the specific enamel-coated coil wire class and diameter depends on the application's electrical and thermal requirements.