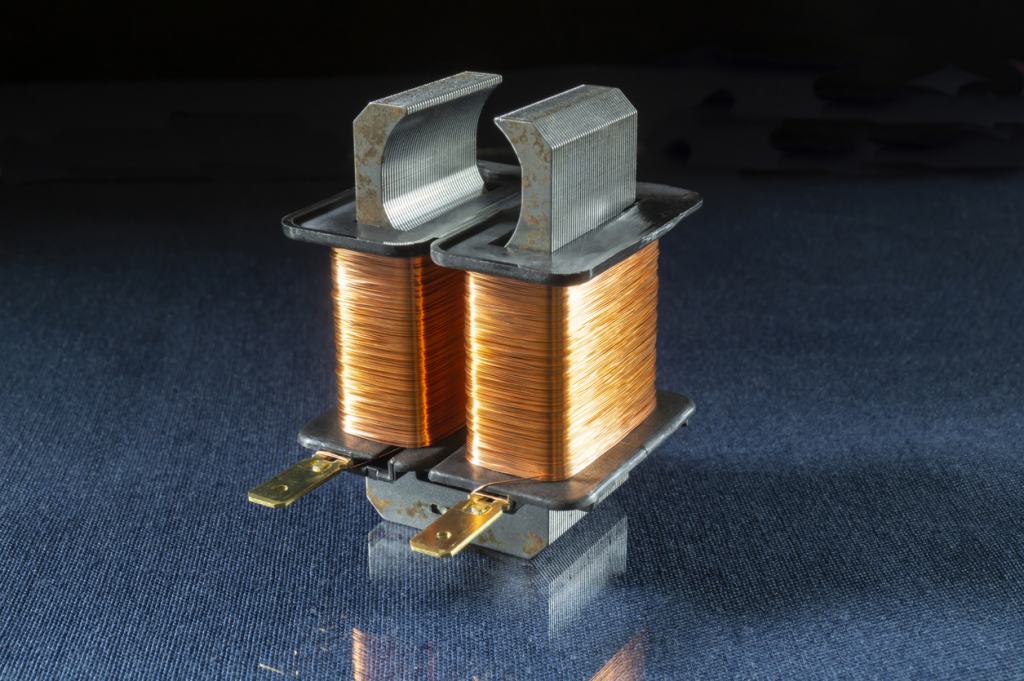
A transformer is an electromagnetic device that converts electrical energy from one voltage level or current value to another. Transformers are commonly used in electricity transmission and distribution, power distribution systems, and many electrical devices.
Key functions and features of transformers include:
- Voltage and Current Transformation: Transformers can change voltage and current values by adjusting the turns ratio between the primary (input) and secondary (output) windings. This allows the use of different voltage levels for electricity transmission and distribution.
- Magnetic Core: Transformers contain a magnetic core that enhances the transmission of the magnetic field, increasing efficiency.
- Magnetic Field Generation: Alternating current passing through the primary winding creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field is linked to the secondary winding to transmit energy.
- Electric Energy Transmission: The magnetic field induces an electrical voltage or current in the secondary winding, representing the transfer of energy from the primary to the secondary winding.
- Isolation and Power Distribution: Transformers provide isolation between different voltage levels and facilitate power distribution.
Transformers play a crucial role in improving energy efficiency and optimizing electrical transmission. By increasing voltage levels along transmission lines and then stepping them down for end-use applications, they minimize energy losses. They also enable devices to receive power at appropriate voltage levels. Transformers are found in various applications, including industrial, commercial, and residential use, and are fundamental components of electrical power systems.