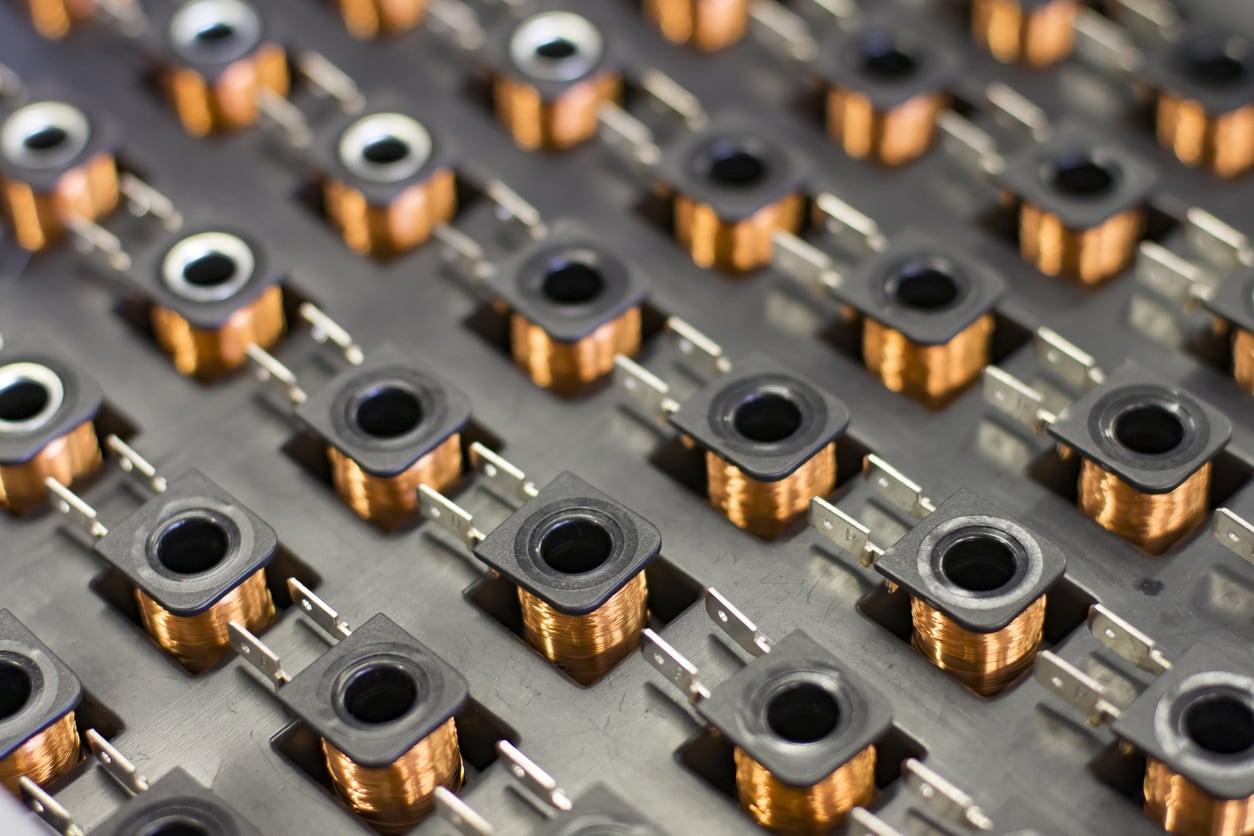
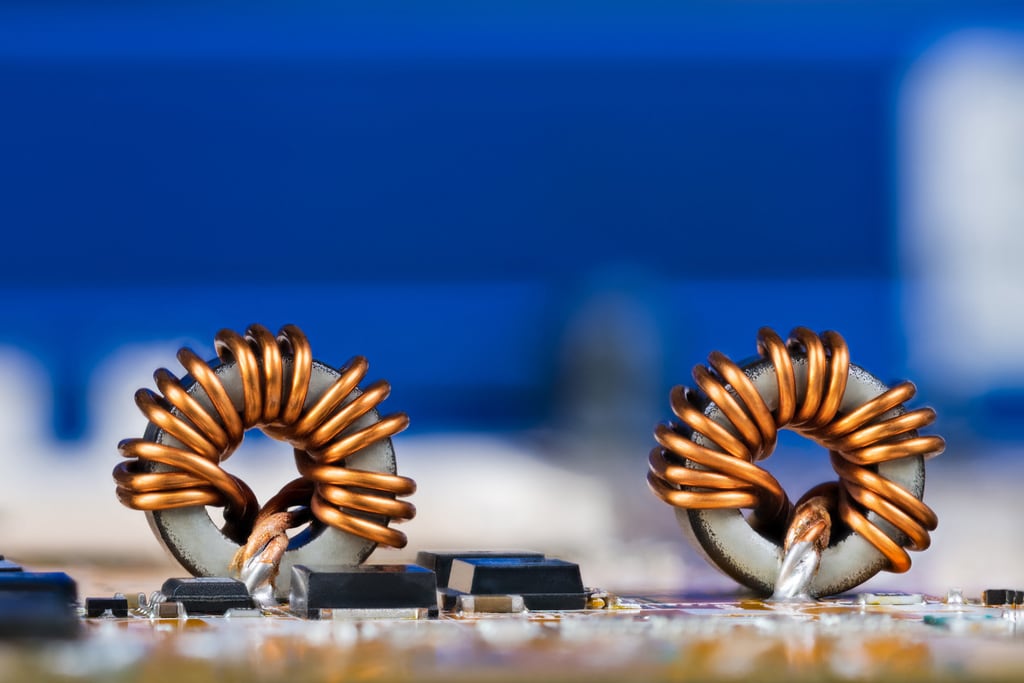
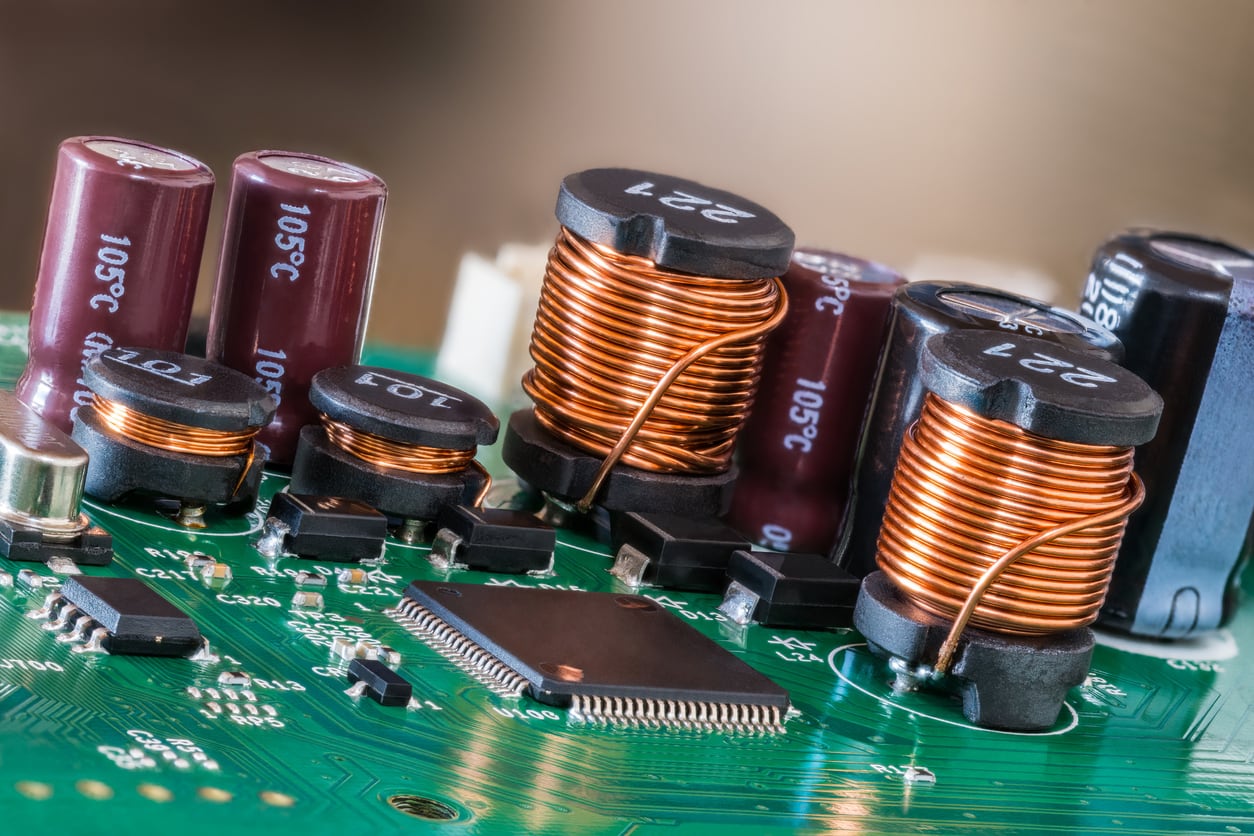
Coil is an electromagnetic component created by winding a wire or another conductor around a core. Coils are commonly used in electrical and electronic circuits to either convert electrical energy into magnetic energy or vice versa.
The primary functions of coils include:
1. Generating a Magnetic Field: When an electric current passes through the wire winding of a coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field fills the space around the coil and stores magnetic energy.
2. Storing Magnetic Energy: Coils have the ability to store magnetic energy. This energy is released when the coil converts electrical energy into magnetic energy or vice versa.
3. Inductance: Coils represent a property called inductance. Inductance is the coil’s ability to generate an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in response to changes in the coil’s magnetic field.
Coils find various applications in electrical and electronic circuits. For example, they are used in transformers, inductors, and coils. Coils play essential roles in applications such as magnetic energy storage, filtering, radio communication, energy conversion, and inductance control. The size, number of windings, and materials used for coils can vary depending on the specific application.